Initiatives for TCFD Recommendations
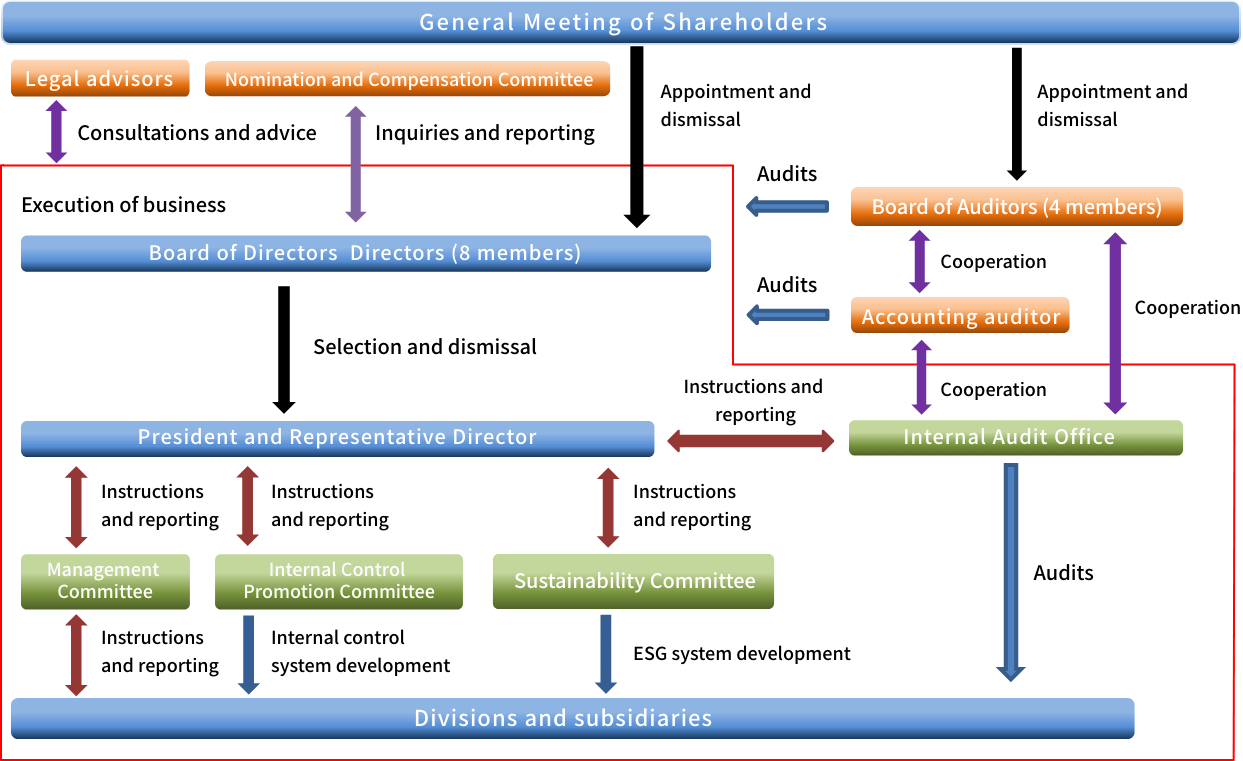
Governance Structure
Board oversight structure
The Board of Directors recognizes that addressing sustainability issues, including climate change, is an important management issue, and established the Sustainability Committee, chaired by the President and CEO, in June 2022 to promote management based on a sustainability perspective. Going forward, the Board of Directors will strengthen its efforts to address sustainability issues by, for example, receiving reports on sustainability issues from the Sustainability Committee at least once a year, including matters related to climate change.
Roles of the management team
In addition, the Executive Committee, which is an advisory body for decision-making by the representative directors and consists of full-time directors, executive officers, general managers, and division managers, will receive reports from the Sustainability Committee on sustainability issues, including climate change-related issues, as appropriate. This will ensure that top management is unified and thoroughly informed about important policies and measures concerning sustainability issues.
Sustainability Committee
In June 2022, we established the Sustainability Committee, chaired by the President and CEO, to promote management based on a sustainability perspective. The Sustainability Committee discusses themes and directions to be addressed over the medium to long term as a company, such as important sustainability issues (materiality), including matters related to climate change, and related sustainability targets, and formulates company-wide policies and targets. The Sustainability Committee also establishes and maintains a system to put these policies and targets into practice, and monitors the status of the initiatives. Major issues discussed and decided by the Sustainability Committee are reported to the Executive Committee and the Board of Directors for supervision and direction.
Strategies
Climate change risks and opportunities and their impact on the organization's business, strategic, and financial plans
We assess the impact of climate change risks and opportunities on our business strategies and financial plans, in addition to understanding the physical and transition risks and business opportunities associated with climate change. In assessing risk, we conduct scenario analysis using two-degree and four-degree scenarios.
In the two-degree scenario, transition risks are considered based on the IEA SDS and other scenarios, and in the four-degree scenario, physical risks are considered based on the IPCC RCP8.5 and other scenarios. Opportunities include the impact on the prices of raw material from stricter government regulations, changing consumer preferences, and rising crude oil prices due to the stagnation of new oil field development. Specifically, the risks associated with stricter government regulations include higher prices for purchased energy such as electricity and gas due to the introduction of a carbon tax, as well as higher raw material prices. Also, tighter regulations for plastics and moves toward decarbonization of the food supply chain are also assumed to be a risk. In addition to the increase in wheat and beef prices and other raw material costs, we will be required to comply with plastics regulations, strengthen initiatives to reduce food waste, and visualize the carbon footprint of raw materials, all of which will increase our response costs.
On the other hand, with regard to changes in consumer preferences, our mainstay yakiniku (grilled meat) business category, which deals with beef with significant GHG emissions, could be significantly affected if consumer preferences change as we move toward a decarbonized society. Regarding the impact on raw material prices of the rise in crude oil prices due to the stagnation of new oil field development, our raw material purchase prices may also be affected through increased production and logistics costs for grains. On the other hand, in the four-degree scenario, we considered mainly physical risks and found that acute risks include the impact on our store facilities, etc. (including the impact of supply chain disruptions) due to increased typhoon intensity and flooding caused by heavy rainfall, the impact on crop prices, etc. resulting from abnormal weather, and the impact on ecosystems caused by rising temperatures. Risks identified include the impact on the price and quality of our raw materials (beef, seafood, vegetables, etc.) due to the effects of rising temperatures on ecosystems.
Resilience of organizational strategies considering different climate-related scenarios, including two-degree scenarios and those below that
We will share the risks identified in the two- and four-degree scenarios with the relevant departments within the company and take appropriate measures to ensure the resilience of our business to climate change risks, and at the same time, to secure our advantages (business opportunities) as one of our strengths. We will continue to address climate change through scenario analysis, elaboration of the financial impact, and specific reflection of risks, opportunities, and countermeasures in our management plans.
| Scenario | Transition risk | Item | Specific impact on our group | Counter measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Two-degree scenario | Policies and laws | Introduction of carbon tax |
|
|
| Decarbonization of food supply chain |
|
|
||
| Strengthening of plastics regulations |
|
|
||
| Market/ reputation | Changing customer needs |
|
|
|
| Increase in production costs of various logistics and raw materials due to soaring energy costs resulting from stagnant development of new oil fields, etc. |
|
|
||
| Scenario | Physical risk | Item | Specific impact on our group | Counter measures |
| 4-degree scenario | Acute risks | Increased flood risk due to increased intensity of typhoons and increased frequency of heavy rains |
|
|
| Effects of extreme weather conditions in crop-growing areas | Cost increases due to higher raw material costs caused by crop failures |
|
||
| Chronic risks | Rise in average temperature |
|
|
Risk Management
Organization's process for identifying and assessing climate-related risks
Our Sustainability Committee is mainly responsible for identifying and assessing climate change risks and other risks from a medium- to long-term perspective. With regard to risks associated with climate change that have already manifested themselves (mainly physical risks such as typhoons and torrential rainfall), the Internal Control Promotion Committee, consisting of the Compliance and Risk Management Subcommittees, plays a central role in identifying and assessing such risks.
The organization's process for managing climate-related risks
Significant risks, including climate-related risks identified and assessed by the Internal Control Committee or the Sustainability Committee, are reported to and shared with the Board of Directors and the Executive Committee as needed, and appropriate countermeasures are considered. Specifically, among climate change-related risks, risks related to management strategies are discussed at meetings of the Board of Directors and the Executive Committee as necessary, and the departments responsible for dealing with each risk consider how to avoid the occurrence of risk events and how to respond to them if they do occur, through instructions, reporting, and other means.
Integration into the organization's overall risk management
Our company has established the Risk Management Regulations and Crisis Response Manual, in accordance with which the Internal Control Promotion Committee plays a central role in identifying possible risks, including climate change risk, evaluating them and considering countermeasures, and then each responsible department takes action. The status of the situation is confirmed and requisite measures are considered, as necessary, at Executive Committee and Board of Director meetings . Climate change risks and other risks identified by the Sustainability Committee are shared with the Internal Control Promotion Committee as needed.
Indicators and Targets
Indicators used to assess climate-related risks and opportunities
We have adopted the intensity of GHG emissions (Scope 1 and 2) per net sales of our directly operated stores in Japan as an indicator to assess the risks and opportunities related to climate change. The following table shows the trends in our GHG emissions intensity and total GHG emissions. We aim to achieve a 50% reduction from the fiscal 2013 level by fiscal 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2050 through various initiatives aimed at decarbonization, including the use of renewable energy.
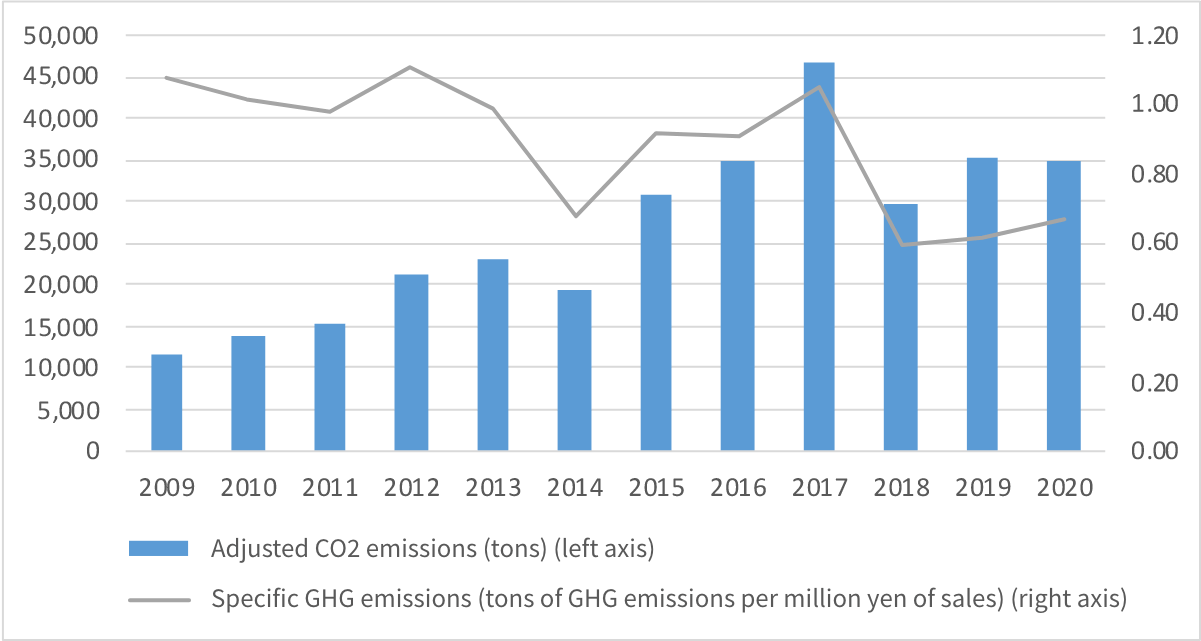
(Note) Scope of GHG emissions is non-consolidated (Monogatari Corporation)
